Install and enable Hyper-V on Windows 10 or 11
Hyper-V can be enabled using the Windows control panel, PowerShell or using the Deployment Imaging Servicing and Management tool (DISM). This article walks through each option.
Requirements
- Windows 10 Enterprise, Pro, Education or a Windows Server
- 64-bit Processor with Second Level Address Translation (SLAT).
- CPU support for VM Monitor Mode Extension (VT-c on Intel CPUs).
- Minimum of 4 GB memory.
- Hardware virtualization support turned on in the BIOS settings
It is not possible to enable Hyper-V on Windows 10 Home.
Enable Hyper-V From the Control Panel
- Right-click on the Windows button and select ‘Apps and Features’.
- Select Programs and Features on the right under related settings.
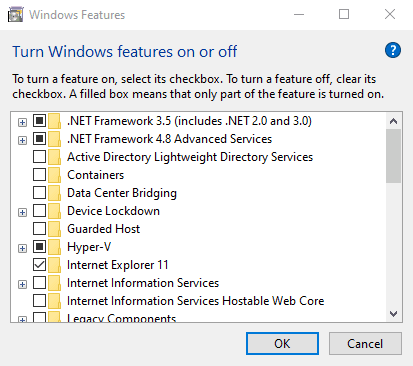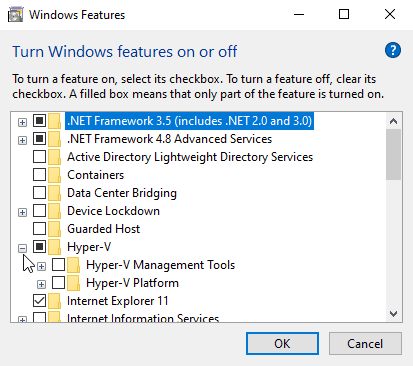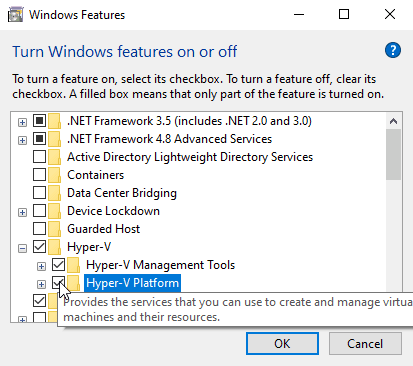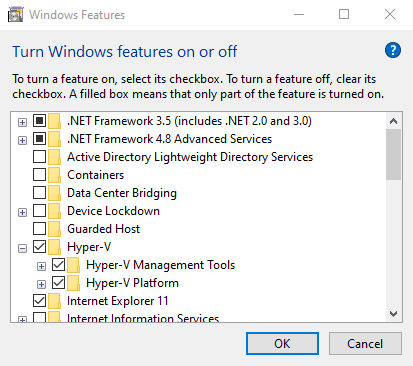
- Select Turn Windows Features on or off.
- Select Hyper-V and click OK.
Wait for the installation to finish and restart your computer as prompted.
Enable Hyper-V using PowerShell
- Open a PowerShell console as Administrator.
- Run the command below:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Hyper-V -AllIf the command couldn’t be found, make sure you’re running PowerShell as Administrator.
Wait for the installation to finish and restart your computer as prompted.
Enable Hyper-V with CMD or Powershell and DISM
The Deployment Image Servicing and Management tool (DISM) helps configure Windows and Windows images.
To enable the Hyper-V role using DISM:
- Open up a PowerShell or CMD session as Administrator.
- Run the command below:
DISM /Online /Enable-Feature /All /FeatureName:Microsoft-Hyper-V